The chart
R
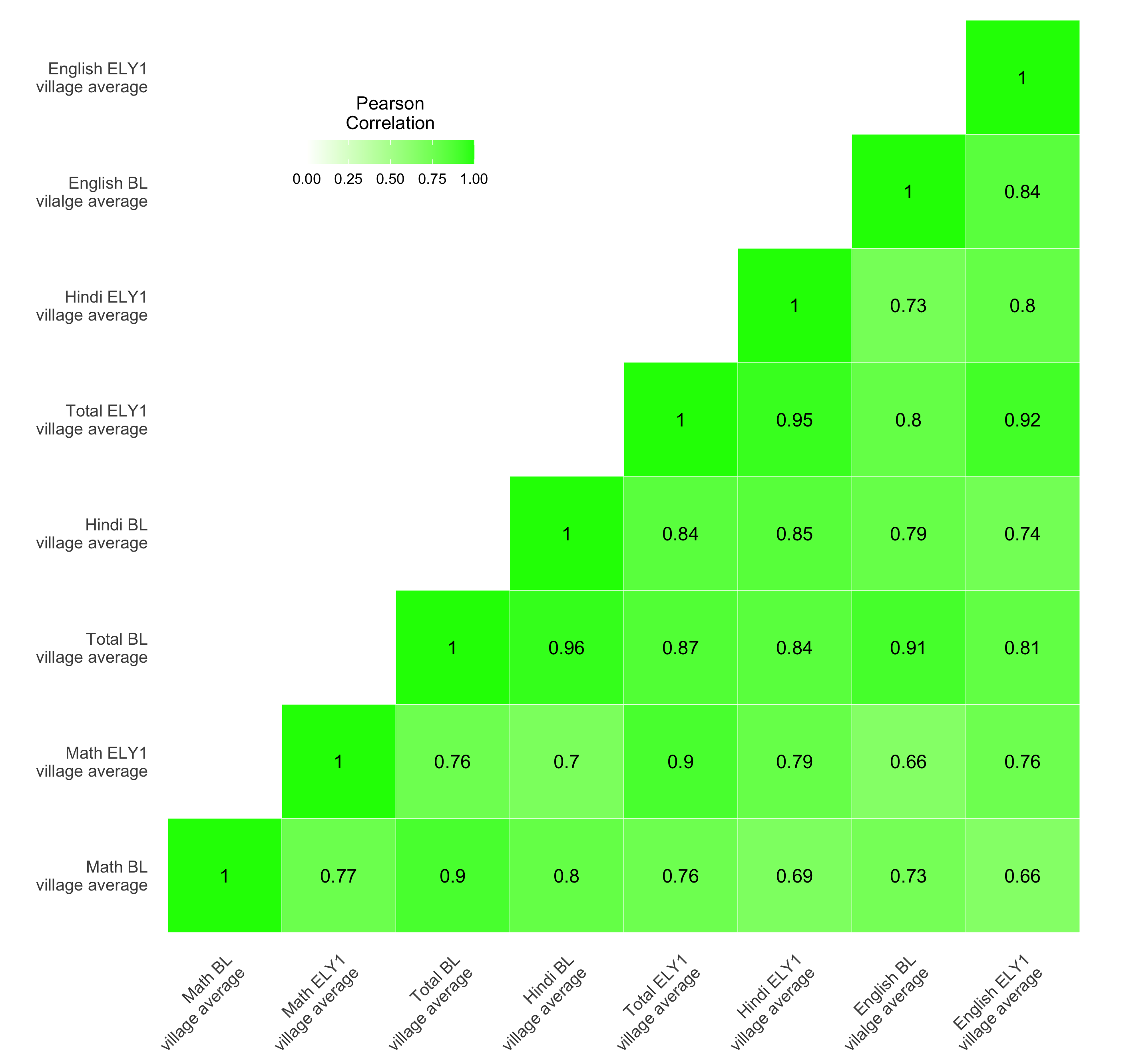
Data
Dataset used to create the R version of the graph can be found here.
The code
R
# Correlogram
############################## Initial Setup ###################################
# Install required packages if they are not already in your system
packages <- c( 'tidyverse', 'reshape2')
lapply(packages, function(i) {if(!i %in% installed.packages() == T)
{install.packages(i, dependencies = TRUE, repos='http://cran.rstudio.com/')}})
# Loading required packages
library("tidyverse")
library("reshape2")
# Setting working directory
setwd("~/Dropbox (IDinsight)/Data visualization library")
############################### Loading dataset ################################
mydata <- read_csv("Data/EG_DIB.csv", show_col_types = FALSE)
################################ Data processing ###############################
# Creating two functions to process the data
# Reordering the correlation matrix
reorder_cormat <- function(cormat){
# Use correlation between variables as distance
dd <- as.dist((1-cormat)/2)
hc <- hclust(dd)
cormat <-cormat[hc$order, hc$order]
}
# Get upper triangle of the correlation matrix
get_upper_tri <- function(cormat){
cormat[lower.tri(cormat)]<- NA
return(cormat)
}
# Creating correlation matrix
# In this example, we are going to focus on the baseline and endline year 1
# scores only
cormat <- mydata %>%
select(ends_with(c("bl_villavg", "ely1_villavg"))) %>%
cor() %>%
round(2)
# Applying functions that we created previously
cormat <- reorder_cormat(cormat)
upper_tri <- get_upper_tri(cormat)
# Reshaping
melted_cormat <- melt(upper_tri, na.rm = TRUE)
############################# Creating the graph ###############################
plot <- melted_cormat %>%
# Setting aesthetic which will be inherited by other geometric objects
ggplot(aes(x = Var2, y = Var1, fill = value))+
# Setting the border color of each tile to white
geom_tile(color = "white") +
# The correlation value is set inside the aesthetic and is being displayed
# in black text color
geom_text(aes(label = value), color = "black", size = 4) +
# Limit kept between zero and one since no pair has negative correlation
scale_fill_gradient2(high = "green",
limit = c(0, 1),
space = "Lab",
name="Pearson\nCorrelation") +
# Creating the x and y axes labels
# \n is a new line character
scale_x_discrete(labels = c("english_ely1_villavg" = "English ELY1\nvillage average",
"math_bl_villavg" = "Math BL\nvillage average",
"total_bl_villavg" = "Total BL\nvillage average",
"hindi_bl_villavg" = "Hindi BL\nvillage average",
"english_bl_villavg" = "English BL\nvilalge average",
"hindi_ely1_villavg" = "Hindi ELY1\nvillage average",
"math_ely1_villavg" = "Math ELY1\nvillage average",
"total_ely1_villavg" = "Total ELY1\nvillage average")) +
scale_y_discrete(labels = c("english_ely1_villavg" = "English ELY1\nvillage average",
"math_bl_villavg" = "Math BL\nvillage average",
"total_bl_villavg" = "Total BL\nvillage average",
"hindi_bl_villavg" = "Hindi BL\nvillage average",
"english_bl_villavg" = "English BL\nvilalge average",
"hindi_ely1_villavg" = "Hindi ELY1\nvillage average",
"math_ely1_villavg" = "Math ELY1\nvillage average",
"total_ely1_villavg" = "Total ELY1\nvillage average"))
plot +
# The following visual elements have been modified:
# x-axis text: Rotated the text to 45 degrees, resized it and changed the
# vertical and horizontal alignment
# y-axis text: Resized
# Removed x and y axis titles
# Removed the plot background
# Removed the axis ticks
# Changed the justification of the legend
# Set the position of the legend
# Changed the direction of the legend to be horizontal
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, vjust = 1,
size = 10, hjust = 1),
axis.text.y = element_text(size = 10),
axis.title = element_blank(),
panel.background = element_blank(),
axis.ticks = element_blank(),
legend.justification = c(1, 0),
legend.position = c(0.35, 0.8),
legend.direction = "horizontal") +
# coord_fixed with ration 1 ensures that the x and y axis scales are 1:1
coord_fixed(ratio = 1) +
# Changed the position of the legend title, horizontal alignment, bar width
# and bar height
guides(fill = guide_colorbar(barwidth = 7, barheight = 1,
title.position = "top", title.hjust = 0.5))
############################# Saving and exporting #############################
# indicating the export folder and the image file name
export_folder <- "R/Other graphs/Exports/"
img_name <- "correlogram_R.png"
ggsave(paste(export_folder,img_name,sep = ""))
Other details
R
Code written by Arkadeep Bandyopadhyay.